The Domain Name System (DNS) translates domain names into IP addresses. It enables users to access websites using easy-to-remember names.
DNS is a crucial component of the internet’s infrastructure. It acts as a directory service, converting human-readable domain names into machine-readable IP addresses. This process is vital for internet navigation, allowing users to access websites without memorizing numerical IP addresses.
DNS servers handle these translations and ensure efficient routing of internet traffic. A well-functioning DNS is essential for seamless online experiences, impacting website loading times and overall accessibility. Understanding DNS helps in optimizing web performance and enhancing user satisfaction. Whether for personal browsing or business operations, DNS plays an indispensable role in the digital landscape.
➡️What is DNS?
The Domain Name System (DNS) is like the phonebook of the internet. People access websites using domain names, like www.example.com. Web browsers interact through Internet Protocol (IP) addresses. DNS translates these domain names to IP addresses so browsers can load Internet resources.
Basic Functionality
The basic functionality of DNS is to convert human-friendly domain names into computer-friendly IP addresses. Without DNS, we would need to remember complex numerical addresses for each website.
Here’s how DNS works:
- A user types a domain name into their browser.
- The browser sends a query to a DNS resolver.
- The resolver checks its cache for the IP address.
- If not cached, the resolver queries a root DNS server.
- The root server directs the resolver to a Top-Level Domain (TLD) server, like .com or .net.
- The TLD server directs the resolver to the authoritative name server for the domain.
- The authoritative server returns the IP address to the resolver.
- The resolver returns the IP address to the browser.
- The browser uses the IP address to access the website.
Without this process, users would have to remember and enter IP addresses, making the internet less user-friendly.
Key Components
DNS has several key components that work together to ensure users can access websites effortlessly. These include:
- DNS Resolver: Acts as an intermediary between the user and the DNS system. It starts the process of converting domain names to IP addresses.
- Root Name Servers: First step in translating human-readable names into IP addresses. They direct queries to the appropriate TLD servers.
- Top-Level Domain (TLD) Servers: Manage domains under a specific extension, like .com or .org. They guide queries to the correct authoritative name servers.
- Authoritative Name Servers: Provide the final answer for the domain name query. They store the actual IP address of the domain.
Here’s a table summarizing the key components of DNS:
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| DNS Resolver | Initiates the DNS query process |
| Root Name Server | Directs queries to TLD servers |
| TLD Server | Manages domains under specific extensions |
| Authoritative Name Server | Provides the final IP address |
These components work together to ensure that users can easily navigate the internet using simple domain names instead of complicated IP addresses.
➡️How DNS Works
The Domain Name System (DNS) is the backbone of the internet, translating human-friendly domain names into IP addresses. This process ensures that users can easily navigate the web without remembering complex numerical strings. Understanding how DNS works is crucial for anyone who wants to grasp the fundamentals of internet infrastructure.
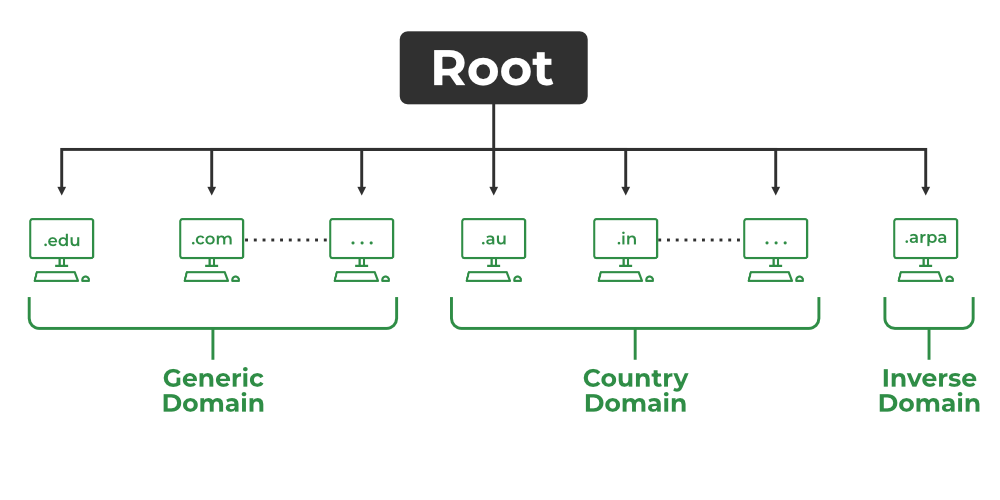
Domain Hierarchy
The DNS operates within a hierarchical structure. This structure ensures efficient and organized domain name resolution. The hierarchy consists of several levels:
- Root Level: This is the top level of the DNS hierarchy. It consists of 13 root servers around the world. They manage the root zone, which contains pointers to the top-level domains (TLDs).
- Top-Level Domains (TLDs): TLDs are the next level below the root. Common TLDs include .com, .org, .net, and country-code TLDs like .uk and .jp. Each TLD has its own authoritative servers.
- Second-Level Domains: These are directly below the TLDs. For example, in the domain example.com, “example” is the second-level domain.
- Subdomains: Subdomains are parts of a larger domain. For example, blog.example.com is a subdomain of example.com.
Each level in the hierarchy has its own set of authoritative servers that store the DNS records. This hierarchical structure helps in managing and resolving domain names efficiently.
Resolution Process
The resolution process in DNS translates domain names into IP addresses. This process involves several steps:
- Query Initiation: The process starts when a user types a domain name into their browser. The browser sends a query to the local DNS resolver.
- Local DNS Resolver: The local DNS resolver checks its cache to see if it has the IP address for the domain. If not, it proceeds to query other DNS servers.
- Root Server Query: The local DNS resolver sends a query to one of the root servers. The root server responds with the authoritative TLD server’s address.
- TLD Server Query: The resolver then queries the TLD server. The TLD server responds with the authoritative server for the second-level domain.
- Authoritative Server Query: Finally, the resolver queries the authoritative server for the second-level domain. This server provides the IP address for the domain name.
- Response to Client: The local DNS resolver caches the IP address and sends it back to the user’s browser. The browser can now connect to the web server using the IP address.
This multi-step process ensures that domain names are accurately translated into IP addresses, enabling seamless internet navigation.
➡️Types of DNS Records
The Domain Name System (DNS) is like the phonebook of the internet. It helps translate human-friendly domain names into IP addresses that computers understand. There are different types of DNS records, each serving a unique purpose. Understanding these records is essential for managing a website effectively. Let’s explore the most common types: A Records, CNAME Records, and MX Records.
Records
Records, or Address Records, are fundamental in the DNS system. They map a domain name to an IP address. This is crucial for directing traffic to the correct server. When a user types a domain name into their browser, the A Record tells the browser which IP address to visit.
Here are some key points about A Records:
- Simple and Direct: A Records provide a straightforward way to connect a domain to an IP address.
- IPv4 Addresses: They use IPv4 addresses, which are numerical labels like 192.0.2.1.
- Single Domain: Each A Record can only point to one IP address.
Below is a simple table illustrating an A Record:
| Domain | IP Address |
|---|---|
| example.com | 192.0.2.1 |
In essence, A Records are the backbone of DNS, ensuring users land on the right website.
Cname Records
CNAME Records, or Canonical Name Records, are used to alias one domain name to another. This is useful for pointing multiple domain names to a single canonical domain.
Consider these important aspects of CNAME Records:
- Alias Domains: CNAME Records allow one domain to point to another.
- Flexibility: They provide flexibility in managing domain names and subdomains.
- No IP Addresses: Unlike A Records, CNAME Records do not map to IP addresses directly.
Here is an example of a CNAME Record:
| Alias Domain | Canonical Domain |
|---|---|
| www.example.com | example.com |
By using CNAME Records, you can simplify DNS management and ensure consistency across domains.
Mx Records
MX Records, or Mail Exchange Records, are essential for email delivery. They specify the mail servers responsible for receiving emails on behalf of a domain.
Important details about MX Records include:
- Email Routing: MX Records direct emails to the correct mail servers.
- Priority Levels: They can have priority levels to determine the order of servers.
- Domain-Specific: MX Records are specific to domains, ensuring emails reach the right destination.
Here’s an example of an MX Record:
| Domain | Mail Server | Priority |
|---|---|---|
| example.com | mail.example.com | 10 |
MX Records are vital for reliable email communication, ensuring emails are directed to the correct servers efficiently.
➡️DNS Security
The Domain Name System (DNS) is the backbone of the internet, translating human-readable domain names into IP addresses. But this vital system is vulnerable to attacks. DNS Security aims to protect DNS infrastructure from malicious activities. Understanding threats and implementing security measures are essential for maintaining a safe and reliable internet.
Common Threats
DNS faces many threats that can disrupt online activities. Some of the common threats include:
- DNS Spoofing: Attackers send fake responses to DNS queries, redirecting users to malicious sites.
- DNS Cache Poisoning: Attackers corrupt the DNS cache, causing users to visit fraudulent sites.
- DDoS Attacks: Distributed Denial of Service attacks overwhelm DNS servers, causing them to crash.
- DNS Tunneling: Attackers use DNS queries to transmit data secretly, bypassing security controls.
These threats can lead to data theft, financial loss, and damage to reputation. Here’s a table summarizing the threats:
| Threat | Description |
|---|---|
| DNS Spoofing | Redirects users to malicious sites |
| DNS Cache Poisoning | Corrupts DNS cache with fraudulent data |
| DDoS Attacks | Overloads DNS servers |
| DNS Tunneling | Transmits data secretly |
Security Measures
Implementing security measures can protect DNS from these threats:
- DNSSEC (Domain Name System Security Extensions): Adds cryptographic signatures to DNS data to verify its authenticity.
- Firewalls: Block malicious traffic and unauthorized access to DNS servers.
- Rate Limiting: Controls the number of queries a server processes, mitigating DDoS attacks.
- Regular Updates: Keeps DNS software up-to-date to protect against known vulnerabilities.
Here’s how these measures work:
- DNSSEC prevents attackers from tampering with DNS data.
- Firewalls provide an extra layer of protection against attacks.
- Rate Limiting ensures servers do not get overwhelmed.
- Regular Updates ensure the latest security patches are applied.
Adopting these measures can significantly enhance DNS security, ensuring a safer browsing experience for users.
➡️DNS in Internet Performance
The Domain Name System (DNS) is a crucial component of the internet. It translates human-readable domain names into IP addresses. This system acts like a phonebook for the web. DNS plays a significant role in internet performance, affecting both speed and reliability. Understanding how DNS impacts internet performance can help users and businesses optimize their online experiences.
Impact On Speed
DNS can greatly impact the speed of internet connections. A fast DNS lookup means quicker access to websites. Here are some ways DNS affects speed:
- Query Response Time: Fast DNS servers respond quicker to queries, reducing the time it takes to load a web page.
- Geographical Proximity: DNS servers closer to the user provide faster responses. This minimizes latency.
- Cached Responses: DNS caching stores previously resolved queries. This speeds up access to frequently visited sites.
Slow DNS servers can lead to delays. Users experience longer wait times when accessing web pages. Companies with slow DNS can lose customers due to poor performance.
Here is a table showing the impact of DNS response time on website speed:
| DNS Response Time | Website Load Time |
|---|---|
| 10ms | Fast |
| 50ms | Moderate |
| 100ms | Slow |
Load Balancing
DNS also helps in load balancing, distributing traffic across multiple servers. This ensures optimal performance and reliability. Here are some key points:
- High Availability: By distributing traffic, DNS ensures that no single server gets overwhelmed. This leads to higher availability.
- Reduced Latency: Traffic is directed to the nearest server, reducing the time data travels and improving speed.
- Failover Protection: If one server fails, DNS reroutes traffic to another server. This maintains continuous service.
Load balancing through DNS is essential for large websites. It ensures that users get fast and reliable access. Without load balancing, servers can become bottlenecks. This results in slow performance and potential downtime.
Here’s a table showing the benefits of DNS load balancing:
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| High Availability | More uptime |
| Reduced Latency | Faster access |
| Failover Protection | Continuous service |

Credit: cyberhoot.com
➡️DNS Management Tools
The Domain Name System (DNS) is essential for translating human-friendly domain names into IP addresses. Managing DNS settings can be complex without the right tools. DNS Management Tools simplify this process by providing user-friendly interfaces and automated features. These tools ensure your website runs smoothly and remains accessible to users worldwide.
Popular Tools
Several DNS management tools are available to help you effectively manage your DNS settings. These tools offer various features, from basic record management to advanced monitoring and reporting. Here are some popular DNS management tools:
- Cloudflare DNS: Known for its speed and security, Cloudflare DNS offers an easy-to-use interface and robust features.
- Amazon Route 53: This tool provides scalable DNS management with routing and failover options.
- Google Cloud DNS: A reliable and scalable DNS service that integrates well with other Google Cloud services.
- Dyn Managed DNS: Offers advanced features like traffic management and security enhancements.
- NS1: Provides intelligent DNS and traffic management solutions.
Each tool has unique features tailored to different needs:
| Tool | Key Features | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Cloudflare DNS | Speed, Security, Easy Interface | General Use |
| Amazon Route 53 | Scalability, Routing, Failover | Large Enterprises |
| Google Cloud DNS | Reliability, Integration | Google Cloud Users |
| Dyn Managed DNS | Traffic Management, Security | Advanced Users |
| NS1 | Intelligent DNS, Traffic Management | Tech-Savvy Users |
Configuration Tips
To get the most out of your DNS management tools, follow these configuration tips:
- Regularly Update Records: Keep your DNS records up-to-date to avoid downtime and connectivity issues.
- Use TTL Wisely: Set appropriate Time-To-Live (TTL) values to balance load and speed.
- Enable DNSSEC: Secure your DNS by enabling DNS Security Extensions (DNSSEC) to prevent attacks.
- Monitor DNS Performance: Use monitoring features to track the performance and health of your DNS.
- Implement Failover Strategies: Configure failover options to ensure your website remains accessible during server failures.
- Document Changes: Keep a log of all changes made to your DNS settings for future reference.
Following these tips can enhance your website’s performance and security:
- Regular updates prevent outdated records from causing issues.
- Proper TTL settings balance between load management and quick updates.
- DNSSEC adds a layer of security to your DNS.
- Monitoring helps identify and resolve issues promptly.
- Failover strategies ensure your site remains up even if a server goes down.
- Documentation aids in troubleshooting and auditing changes.
Using these tips ensures your DNS is optimized, secure, and reliable.
➡️Future of DNS
The Domain Name System (DNS) acts like the phone book of the internet. It translates human-readable domain names into IP addresses. As the internet evolves, the future of DNS is poised for significant changes. These changes will make it faster, more secure, and more reliable.
Emerging Technologies
The future of DNS will be shaped by several emerging technologies. These technologies promise to enhance the functionality and security of DNS.
1. DNS over HTTPS (DoH):
- Encrypts DNS queries to improve privacy.
- Prevents eavesdropping and manipulation of DNS data.
2. DNS over TLS (DoT):
- Provides a secure channel for DNS queries.
- Uses Transport Layer Security (TLS) to encrypt data.
3. Quantum Computing:
- Could potentially break current encryption methods.
- Requires new, quantum-resistant algorithms for DNS security.
4. Blockchain Technology:
- Offers decentralized and tamper-proof DNS solutions.
- Enhances the security and reliability of DNS records.
Trends To Watch
Several trends are emerging that will shape the future of DNS. These trends focus on security, speed, and scalability.
1. Increased Adoption of DoH and DoT:
- More organizations will adopt these technologies.
- Improves user privacy and data security.
2. Growing Importance of DNS Security:
- DNS security will become a top priority.
- Organizations will invest in advanced security measures.
3. Focus on Reducing Latency:
- Efforts to reduce DNS query latency will increase.
- Improves user experience and website performance.
4. Adoption of IPv6:
- IPv6 adoption will continue to grow.
- Supports a larger number of devices and improves DNS efficiency.
5. AI and Machine Learning:
- AI will help in predictive DNS query resolution.
- Machine learning algorithms will improve DNS security.

Credit: kinsta.com
➡️Troubleshooting DNS Issues
The Domain Name System (DNS) is a critical component of the internet. It converts human-readable domain names into IP addresses. Sometimes, DNS issues can disrupt this process, causing websites to be unreachable. Troubleshooting DNS problems can resolve these issues quickly. This guide will help you understand common DNS problems and the diagnostic tools you can use.
Common Problems
DNS issues come in many forms. Here are some of the most common problems:
- DNS Server Not Responding: The server might be down or unreachable.
- Incorrect DNS Settings: Misconfigured DNS settings can lead to resolution failures.
- DNS Cache Corruption: A corrupted cache can store incorrect data.
- Network Connectivity Issues: Problems with your internet connection can impact DNS resolution.
- ISP DNS Issues: Your Internet Service Provider’s DNS might be having problems.
Sometimes, DNS issues can also be due to malware or viruses. Ensuring that your system is clean can help mitigate these problems. Here’s a quick table summarizing these issues and their potential solutions:
| Problem | Potential Solution |
|---|---|
| DNS Server Not Responding | Check server status, use alternative DNS servers |
| Incorrect DNS Settings | Verify and correct DNS configuration |
| DNS Cache Corruption | Clear DNS cache |
| Network Connectivity Issues | Check and restore network connection |
| ISP DNS Issues | Switch to a public DNS service |
Diagnostic Tools
Several tools can help diagnose DNS problems. Here are some essential ones:
- Ping: This tool tests connectivity to a server. It helps determine if the server is reachable.
- Traceroute: Traceroute shows the path data takes to reach a destination. It helps identify where the connection is failing.
- nslookup: This command-line tool queries DNS to obtain domain name or IP address mapping. It helps verify DNS records.
- dig: Similar to nslookup, dig provides detailed DNS query information. It’s useful for advanced troubleshooting.
- DNS Benchmarks: Tools like “DNS Benchmark” test the speed and reliability of DNS servers. They help choose the best DNS server.
Below is a brief overview of these tools and their uses:
| Tool | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Ping | Tests server connectivity |
| Traceroute | Identifies path and points of failure |
| nslookup | Queries DNS records |
| dig | Provides detailed DNS query info |
| DNS Benchmark | Tests DNS server speed and reliability |
Using these tools can help identify and fix DNS issues quickly. Always start with basic checks and move to advanced tools if needed.
➡️Summary
The Domain Name System (DNS) is like the phone book of the internet. It translates domain names to IP addresses, allowing browsers to load internet resources. Understanding DNS is crucial for anyone who uses the internet. This final thought section wraps up the key takeaways about DNS.
Importance of Dns
DNS is essential for the internet. Without DNS, we would have to remember IP addresses instead of domain names. This would be complex and inefficient.
Security is a major concern in DNS. Cyberattacks like DNS spoofing can redirect users to malicious sites. Implementing DNSSEC (DNS Security Extensions) helps protect against these threats. Always ensure your DNS is secure.
Dns Performance
Performance matters in DNS. Slow DNS can lead to slow website loading times. Use reliable DNS servers to improve speed. Consider using services like Google Public DNS or Cloudflare DNS for better performance.
DNS Management
Managing DNS records is vital for website management. Proper DNS management ensures website availability. Use DNS management tools to keep track of records.
The future of DNS looks promising with advancements in technology. DNS over HTTPS (DoH) and DNS over TLS (DoT) aim to enhance privacy and security. Stay updated with these changes to keep your DNS robust.
Quick DNS Tips
- Always use secure DNS servers.
- Regularly update your DNS records.
- Monitor DNS performance.
- Stay informed about DNS security threats.
Overall, DNS is a fundamental part of the internet. Ensuring its security and performance is crucial. Understanding DNS helps navigate the digital world more efficiently.
Credit: www.geeksforgeeks.org
➡️Frequently Asked Questions
- What Is Dns?
Ans: DNS stands for Domain Name System. It translates domain names to IP addresses. This process makes it easier for users to access websites using human-readable names.
- How Does Dns Work?
Ans: DNS works by converting domain names into IP addresses. When you type a domain name, DNS servers find the corresponding IP address, allowing your browser to load the website.
- Why is DNS important?
Ans: DNS is crucial for the internet’s functionality. It simplifies user navigation by translating human-readable domain names into machine-readable IP addresses, ensuring seamless access to websites.
- What are DNS Records?
Ans: DNS records are instructions within the DNS. They provide information about a domain, including its IP address, mail server, and other essential details required for Internet communication.
➡️Final Thought
Understanding the Domain Name System (DNS) is crucial for a seamless online experience. It translates domain names into IP addresses, enabling efficient internet navigation. Proper DNS management can enhance website performance and security. Stay informed and optimize your DNS settings to ensure a reliable and fast web presence.




