Blockchain Technology is a decentralized digital ledger technology. It ensures secure and transparent transactions across a network of computers.
Blockchain revolutionizes industries by providing a secure, transparent, and tamper-proof way to record transactions. This technology operates without a central authority, which increases trust and reduces fraud. Each transaction is recorded in a block and linked to the previous one, forming a chain.
This structure makes it difficult for unauthorized changes to occur. Blockchain is widely used in cryptocurrencies, supply chain management, and smart contracts. Its ability to streamline processes and enhance security makes it a valuable tool for various sectors. As adoption grows, Distributed Ledger Technology continues to transform how businesses operate and interact.
➡️What is Blockchain?
Blockchain is a revolutionary technology that has transformed how we handle transactions. But what is Blockchain? It is a decentralized digital ledger that records transactions across many computers. This ensures that the record cannot be altered retroactively without altering all subsequent blocks and the consensus of the network.
Core Concepts
Understanding Blockchain starts with its core concepts. These concepts lay the foundation for how it operates and why it is secure.
1. Decentralization: Blockchain eliminates the need for a central authority. All participants in the network have access to the entire database and its complete history. This ensures transparency and trust.
2. Distributed Ledger: A distributed ledger is a database that is consensually shared and synchronized across multiple sites, institutions, or geographies. This allows transactions to have public “witnesses,” enhancing security.
3. Cryptographic Hash Function: Each block in the Blockchain contains a cryptographic hash of the previous block. This creates a chain of blocks, enhancing data integrity.
4. Consensus Mechanisms: Consensus mechanisms are algorithms used to achieve agreement on a single data value among distributed processes. Popular mechanisms include Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS).
Key Features
Blockchain’s key features make it unique and powerful. These features contribute to its growing adoption in various industries.
- Immutability: Once data is written to a Blockchain, it is extremely difficult to change. This makes it a trustworthy source of information.
- Transparency: All transactions are visible to participants in the network. This promotes trust and accountability.
- Security: Blockchain uses advanced cryptographic techniques to secure data. This makes it resistant to hacking.
- Decentralization: There is no central point of control. This reduces the risk of failure and makes the system more robust.
- Smart Contracts: Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. They automatically enforce and execute the terms of the contract.
These features make Blockchain a groundbreaking technology with endless possibilities.
Credit: blogs.iadb.org
➡️How Blockchain Works
Blockchain is a revolutionary technology that enables secure and transparent transactions. Understanding how it works is essential to grasp its impact. It involves a series of processes that ensure data integrity and trust without intermediaries.
Transaction Process
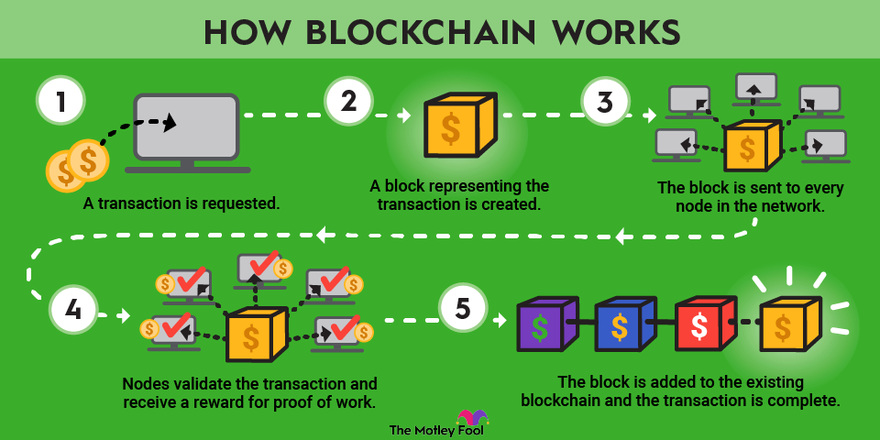
In a Blockchain, the transaction process is vital. It starts when someone requests a transaction. This transaction could involve cryptocurrency, contracts, records, or other information. The transaction details are then broadcasted to a network of peer-to-peer computers, known as nodes.
Each node validates the transaction using algorithms. Once verified, the transaction is combined with other transactions to create a new block of data for the ledger. This new block is then added to the existing Blockchain in a way that is permanent and unalterable.
- Step 1: Request a transaction.
- Step 2: Broadcast the transaction to the network.
- Step 3: Validate the transaction by nodes.
- Step 4: Combine validated transactions into a new block.
- Step 5: Add the new block to the Blockchain.
After adding the new block, the transaction is complete. The entire process ensures that the data is secure, transparent, and tamper-proof.
Consensus Mechanisms
The consensus mechanism is crucial for Blockchain. It ensures all nodes agree on the validity of transactions. There are several types of consensus mechanisms, each with its unique approach.
Proof of Work (PoW) is the most well-known. In PoW, miners solve complex mathematical problems to validate transactions. The first miner to solve the problem gets to add the block to the Blockchain and receives a reward.
Proof of Stake (PoS) is another method. Instead of solving problems, validators are chosen based on the number of coins they hold. The more coins, the higher the chance of being selected to validate transactions and earn rewards.
| Consensus Mechanism | Key Feature |
|---|---|
| Proof of Work (PoW) | Solves mathematical problems |
| Proof of Stake (PoS) | Validators chosen by coin holding |
Both methods ensure the network remains secure and trustworthy. By achieving consensus, Blockchain maintains its integrity and reliability.
➡️Types of Blockchain
Blockchain technology has revolutionized the way we handle data and transactions. There are different types of blockchains, each with its unique features and use cases. Understanding these types is crucial to leveraging it effectively. Let’s explore the three main types: Public Blockchains, Private Blockchains, and Consortium Blockchains.
Public Blockchains
Public blockchains are open to everyone. Anyone can join, participate, and validate transactions. These blockchains are decentralized and transparent. Bitcoin and Ethereum are prime examples of public blockchains.
- Decentralization: No single entity controls the network.
- Transparency: All transactions are visible to anyone.
- Security: High level of security due to its decentralized nature.
- Open participation: Anyone can join and contribute.
- Trustless environment: No need to trust a central authority.
- Immutability: Transactions cannot be altered once added.
- Scalability issues: Handling a large number of transactions can be slow.
- High energy consumption: Mining requires significant computational power.
Private Blockchains
Private blockchains, also known as permissioned blockchains, are restricted. Only selected participants can join and validate transactions. These blockchains are often used by businesses and organizations for internal purposes.
- Controlled access: Only authorized participants can access the network.
- Privacy: Transactions are visible only to authorized members.
- Efficiency: Faster transaction processing due to fewer participants.
- Enhanced privacy: Sensitive data is protected from public view.
- Better scalability: More efficient handling of transactions.
- Cost-effective: Lower energy consumption compared to public blockchains.
- Centralization risks: A single entity may control the network.
- Trust issues: Participants must trust the controlling entity.
- Limited transparency: Lack of public oversight.
Consortium Blockchains
Consortium blockchains are a blend of public and private blockchains. They are controlled by a group of organizations rather than a single entity. These blockchains are ideal for collaborative efforts across different entities.
- Group control: Multiple organizations manage the network.
- Semi-decentralization: Combines elements of decentralization and centralization.
- Shared governance: Decisions are made collectively by the consortium members.
- Collaboration: Facilitates cooperation between different organizations.
- Efficiency: Faster and more scalable than public blockchains.
- Security: Higher security due to shared control.
- Complex governance: Decision-making can be complex and slow.
- Trust issues: Members must trust each other to some extent.
- Limited access: Not open to the public.
➡️Blockchain Applications
Blockchain technology has revolutionized various industries by providing a secure, transparent, and decentralized way of recording transactions. Blockchain applications are vast and continually growing, impacting areas from finance to healthcare. Below are some key applications of blockchain technology.
Cryptocurrencies
Cryptocurrencies are the most well-known application of blockchain technology. Bitcoin, the first cryptocurrency, introduced the world to a decentralized form of digital currency. Since then, numerous cryptocurrencies have emerged, each with unique features and uses.
Key features of cryptocurrencies include:
- Decentralization: No central authority controls the currency.
- Security: Transactions are secured using cryptography.
- Transparency: Transaction details are public and easily verifiable.
- Immutability: Once recorded, transactions cannot be altered.
Popular cryptocurrencies include:
| Name | Symbol | Market Cap |
|---|---|---|
| Bitcoin | BTC | $1 Trillion |
| Ethereum | ETH | $400 Billion |
| Ripple | XRP | $50 Billion |
Cryptocurrencies provide a new way of conducting financial transactions, offering greater control and privacy to users. They are changing the landscape of traditional finance.
Supply Chain Management
Supply Chain Management benefits significantly from blockchain technology. It provides transparency and traceability in the movement of goods from manufacturers to consumers. This technology helps track every step of the supply chain, ensuring product authenticity and quality.
Advantages of blockchain in supply chain management include:
- Improved Transparency: All parties can see the product journey.
- Enhanced Traceability: Easily trace the origin of products.
- Increased Efficiency: Streamlined processes reduce delays.
- Fraud Prevention: Difficult to manipulate records.
Industries using blockchain for supply chain:
| Industry | Use Case |
|---|---|
| Food & Beverage | Tracking food safety and origins |
| Pharmaceuticals | Ensuring drug authenticity |
| Fashion | Verifying product authenticity |
Blockchain technology enhances the reliability and efficiency of supply chains, ensuring consumers receive high-quality, authentic products.
Healthcare
Healthcare is another field where blockchain technology is making a significant impact. Blockchain enhances the security, privacy, and interoperability of health data. It provides a secure and transparent way to store and share medical records.
Benefits of blockchain in healthcare include:
- Data Security: Protects patient information from breaches.
- Interoperability: Enables seamless data sharing across systems.
- Transparency: Patients have better access to their records.
- Data Integrity: Ensures the accuracy of medical records.
Applications of blockchain in healthcare:
- Electronic Health Records (EHRs): Secure and accessible patient records.
- Drug Traceability: Tracking drugs from manufacturer to patient.
- Clinical Trials: Ensuring the integrity of trial data.
Blockchain technology improves the efficiency and security of healthcare services, providing better outcomes for patients and healthcare providers.
➡️Benefits of Blockchain
Blockchain technology has revolutionized the way we think about data and transactions. Its unique structure offers numerous advantages that can transform various industries. Let’s explore the key benefits of Blockchain technology.
Transparency
Blockchain ensures unmatched transparency in all transactions. Every transaction is recorded on a public ledger, visible to everyone. This transparency reduces the risk of fraud and corruption.
Key points of Blockchain transparency:
- Public Ledger: Every transaction is recorded and can be viewed by anyone.
- Immutable Records: Once a transaction is recorded, it cannot be altered.
- Trust: Increased trust between parties due to visible records.
Consider the following table illustrating the transparency features:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Public Ledger | Visible to all participants |
| Immutable Records | Cannot be changed once recorded |
| Trust | Increased trust between parties |
Security
Security is a cornerstone of Blockchain technology. Each transaction is encrypted and linked to the previous one, creating a chain that is nearly impossible to break. This ensures data integrity and protection from cyber threats.
Key security features include:
- Encryption: Transactions are encrypted, making them secure.
- Distributed Network: Data is stored across multiple nodes, reducing the risk of hacking.
- Consensus Mechanisms: Transactions are verified by multiple participants, ensuring legitimacy.
Here’s a table detailing Blockchain security features:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Encryption | Secures transaction data |
| Distributed Network | Reduces hacking risks |
| Consensus Mechanisms | Verifies transactions |
Decentralization
Blockchain operates on a decentralized network. There is no central authority controlling the data, which reduces the risk of failure and manipulation. This decentralization empowers users and ensures fairness.
Key aspects of decentralization include:
- No Central Authority: Control is distributed among all participants.
- Reduced Failure Risk: No single point of failure.
- User Empowerment: Users have more control over their data.
Consider the following table illustrating the decentralization features:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| No Central Authority | Control is distributed |
| Reduced Failure Risk | No single point of failure |
| User Empowerment | More control over data |
➡️Challenges in Blockchain
Blockchain technology is revolutionizing various industries. Yet, despite its promise, there are significant hurdles. These challenges hinder widespread adoption and need to be addressed. In this blog post, we will explore the key challenges in blockchain.
Scalability Issues
Scalability is a major concern in blockchain technology. Current blockchain networks struggle to process a high volume of transactions quickly. This creates delays and inefficiencies. The two primary reasons for scalability issues are:
- Block Size: Each block in the blockchain has a limited size. This restricts the number of transactions it can hold.
- Consensus Mechanism: The process of validating transactions is time-consuming. This slows down the network.
For example, Bitcoin can handle about 7 transactions per second. In contrast, Visa processes around 24,000 transactions per second. This comparison highlights the need for better scalability solutions.
Developers are exploring various methods to improve scalability:
- Sharding: This involves splitting the blockchain into smaller, manageable pieces.
- Layer 2 Solutions: These add another layer to the blockchain to handle more transactions.
- Off-Chain Transactions: Transactions are processed outside the blockchain and later added to it.
Regulatory Concerns
Regulatory concerns pose a significant challenge to blockchain technology. Governments and regulatory bodies have yet to establish clear guidelines. This creates uncertainty for businesses and investors. Key regulatory concerns include:
- Legal Status: The legal status of cryptocurrencies varies by country. This inconsistency creates confusion.
- Compliance: Blockchain must comply with existing financial regulations. This includes anti-money laundering (AML) and know your customer (KYC) requirements.
Some countries have banned cryptocurrencies outright. Others have embraced them with open arms. This regulatory patchwork makes it difficult for blockchain companies to operate globally. Ensuring compliance with different regulations can be costly and time-consuming.
| Country | Regulation |
|---|---|
| USA | Regulated |
| China | Banned |
| Japan | Legal |
Collaboration between governments and blockchain companies is necessary. This will create a balanced regulatory framework that encourages innovation while protecting consumers.
Energy Consumption
Blockchain technology is often criticized for its high energy consumption. This is primarily due to the Proof of Work (PoW) consensus mechanism. PoW requires miners to solve complex mathematical problems. This process consumes a lot of electricity. For instance, the Bitcoin network uses more energy than some entire countries.
High energy consumption has several negative impacts:
- Environmental Impact: Increased carbon footprint due to high energy use.
- Operational Costs: High electricity bills make mining less profitable.
Alternatives to PoW are being explored to reduce energy consumption. These include:
- Proof of Stake (PoS): This method requires validators to hold and stake their coins.
- Proof of Authority (PoA): Validators are pre-approved and trusted entities.
- Hybrid Models: Combining PoW and PoS to balance security and efficiency.
Adopting these alternatives could make blockchain more sustainable. This will pave the way for broader adoption and positive environmental impact.
➡️Future of Blockchain
Blockchain technology is evolving rapidly, promising to revolutionize various industries. The future of Blockchain looks bright, with numerous advancements on the horizon. This technology’s potential extends beyond cryptocurrencies, offering solutions to enhance security, transparency, and efficiency across multiple sectors.
Trends To Watch
Several trends are shaping the future of Blockchain. These trends highlight Blockchain’s growing importance and its transformative impact:
- DeFi (Decentralized Finance): DeFi applications are gaining traction, offering financial services without traditional intermediaries like banks. This trend aims to make financial systems more inclusive and accessible.
- Interoperability: Interoperability between different Blockchain networks is becoming crucial. Solutions like Polkadot and Cosmos are working on connecting multiple Blockchains, enabling seamless communication and data exchange.
- Scalability: Scalability remains a significant challenge. Technologies like Layer 2 solutions, sharding, and new consensus algorithms are being developed to handle increased transaction volumes efficiently.
- Stablecoins: Stablecoins are digital currencies pegged to stable assets like the US Dollar. They offer stability in the volatile crypto market and are increasingly used for transactions and savings.
- Government Regulations: Governments worldwide are recognizing Blockchain’s potential and creating regulatory frameworks. These regulations aim to protect users while fostering innovation.
Potential Innovations
Blockchain’s future is also about potential innovations that could redefine how we interact with technology:
- Smart Contracts: Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms directly written into code. They can automate complex processes, reducing the need for intermediaries and lowering costs.
- Blockchain in Supply Chain: Blockchain can improve supply chain transparency and traceability. It ensures that every product’s journey from origin to consumer is recorded, preventing fraud and ensuring authenticity.
- Healthcare Applications: Blockchain could revolutionize healthcare by securing patient data, ensuring privacy, and improving data sharing across institutions. This could lead to better patient outcomes and streamlined operations.
- Voting Systems: Blockchain-based voting systems promise secure, transparent, and tamper-proof elections. This innovation could enhance trust in democratic processes.
- Identity Management: Blockchain can provide a secure and decentralized way to manage digital identities. This ensures privacy and security, reducing the risks of identity theft and fraud.
Blockchain technology is on a path of continuous growth and innovation. The trends and potential innovations mentioned above are just a glimpse of what’s to come. As Blockchain technology evolves, it will bring about significant changes across various sectors, making the future more secure, transparent, and efficient.

Credit: builtin.com
➡️Getting Started With Blockchain
Blockchain is a revolutionary technology that is changing how we handle data and transactions. It offers a decentralized, secure, and transparent way to store information. Many industries are adopting blockchain to improve their processes. If you are new to blockchain, this guide will help you get started. You’ll learn about essential resources and how to build your first blockchain project.
Learning Resources
To start with blockchain, you need good learning resources. These will help you understand the basics and advanced concepts. Here are some key resources:
- Online Courses: Websites like Coursera, Udemy, and edX offer comprehensive blockchain courses. They cover everything from the basics to advanced topics.
- Books: Some popular books are “Blockchain Basics” by Daniel Drescher and “Mastering Bitcoin” by Andreas M. Antonopoulos. These books provide detailed insights into blockchain technology.
- Blogs and Websites: Websites like CoinDesk and Blockchain.com have regular updates and articles. They help you stay updated with the latest trends.
- Community Forums: Join forums like Reddit, Stack Exchange, and specialized blockchain forums. These communities can answer your questions and provide valuable advice.
Here is a table summarizing these resources:
| Resource Type | Examples |
|---|---|
| Online Courses | Coursera, Udemy, edX |
| Books | Blockchain Basics, Mastering Bitcoin |
| Blogs/Websites | CoinDesk, Blockchain.com |
| Community Forums | Reddit, Stack Exchange |
Building a Project
Once you have a basic understanding, you can start building your own blockchain project. This hands-on experience is invaluable. Follow these steps to get started:
- Choose a Platform: Select a blockchain platform like Ethereum or Hyperledger. Ethereum is great for creating smart contracts.
- Set Up Development Environment: Install necessary tools like Node.js and Truffle for Ethereum. These tools help in coding and testing.
- Write Smart Contracts: Use Solidity to write your smart contracts. Solidity is the programming language for Ethereum.
- Deploy Your Contract: Use tools like Ganache to test your contracts locally. Once tested, deploy them on the Ethereum network.
- Build Front-End: Create a front-end interface using HTML, CSS, and JavaScript. This interface interacts with your blockchain application.
Here is a simple example of a smart contract in Solidity:
pragma solidity ^0.8.0;
contract SimpleStorage {
uint256 public data;
function setData(uint256 _data) public {
data = _data;
}
function getData() public view returns (uint256) {
return data;
}
}
Building a blockchain project might seem daunting, but breaking it into smaller tasks makes it manageable. Start simple and gradually add more features. This approach ensures you learn effectively and build a functional project.
➡️In a Nutshell
Blockchain technology has transformed industries by offering secure, transparent, and decentralized solutions. It has revolutionized finance, supply chains, and healthcare, to name a few. This section will provide a final thought on the impact and future of blockchain technology.
Potential For Future Growth
The potential for blockchain technology remains vast. New applications are emerging daily. The technology is expanding beyond cryptocurrencies. Industries are finding innovative ways to use blockchain for a variety of purposes.
Many experts believe blockchain will be a key component of the future digital economy. It offers significant benefits over traditional systems. It provides enhanced security, transparency, and efficiency.
Challenges To Overcome
Despite its potential, blockchain faces several challenges. Scalability is a major concern. Current blockchain networks struggle to handle large volumes of transactions. This limits their widespread adoption.
Regulatory uncertainty is another hurdle. Governments worldwide are still figuring out how to regulate blockchain technology. This creates uncertainty for businesses and investors.
Real-world Applications
Blockchain is already making an impact in the real world. Many companies are using blockchain for supply chain management. This ensures product authenticity and improves transparency.
In the financial sector, blockchain enables faster and more secure transactions. It reduces the need for intermediaries. This lowers costs and increases efficiency.
Opportunities For Innovation
Blockchain technology presents numerous opportunities for innovation. Developers are creating decentralized applications (DApps) that run on blockchain networks. These DApps offer new functionalities and services that were not possible before.
Smart contracts are another area of innovation. These self-executing contracts automate and enforce agreements. They reduce the need for intermediaries and increase trust between parties.
Blockchain technology is still in its early stages. Its potential is immense, and its impact will grow. As challenges are addressed, blockchain will become more prevalent. The future of blockchain technology looks promising and exciting.
Credit: www.fool.com
➡️Frequently Asked Questions
- What Is Blockchain Technology?
Ans: Blockchain technology is a decentralized digital ledger. It records transactions across multiple computers securely. Each block contains transaction data. This data is immutable and transparent. Blockchain enhances security and reduces fraud.
- How Does Blockchain Work?
Ans: Blockchain works by linking blocks of data using cryptography. Each block contains a cryptographic hash of the previous block. This ensures data integrity and security. Transactions are verified by network nodes through consensus.
- What Are the Benefits of Blockchain?
Ans: Blockchain offers transparency and security. It reduces fraud and ensures data integrity. It also enables decentralized control. This enhances trust and efficiency. Blockchain can streamline various industries, including finance and supply chain.
- Can Blockchain Be Hacked?
Ans: Hacking blockchain is extremely difficult. Its decentralized nature and cryptographic security make it robust. However, vulnerabilities in blockchain applications can be exploited. Proper implementation and security measures are crucial.
➡️Final Thought
Blockchain technology is revolutionizing industries with its transparency and security. Its potential for innovation is immense. As adoption grows, so do the opportunities for businesses. Embrace blockchain to stay ahead of the curve. The future is decentralized, and blockchain is leading the way.
Stay informed and be part of this exciting journey.